Case Study: Small-Parts Unmanned Warehouse Automated Storage and Retrieval System (AS/RS)
2025-07-02
NAEC
NAEC Intelligent Logistics
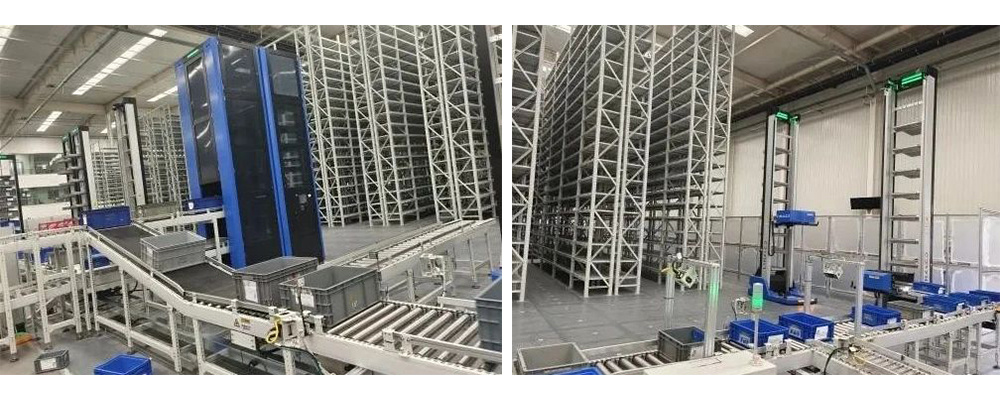

To address the complex inventory management challenges of small parts in manufacturing enterprises, NAEC Intelligent Logistics has developed a comprehensive unmanned warehouse automated storage and retrieval system (AS/RS) solution for a client. This system solves several major pain points in parts inventory management:
01.
High Part Count & Limited Space: The vast number of components required significant storage area. Within the constrained warehouse footprint, dynamic storage location adjustments based on production changes were needed. Existing vertical space utilization was only 32%.
02.
Diverse Parts & Packaging: The variety of part types and shapes, coupled with numerous suppliers using different packaging styles, resulted in complex and mixed incoming container types.
03.
Inefficient Manual Operations: Traditional logistics operations (receiving, putaway, picking, inventory counting) relied heavily on manual labor, leading to low efficiency and risks of errors like mis-picks and missed picks.
To enhance overall logistics automation and intelligence, improve labor efficiency, and reduce production safety and quality risks, NAEC Intelligent Logistics implemented a mini-parts unmanned warehouse AS/RS. This enables highly efficient, fully automated storage operations, significantly reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
Business Processes
NAEC 1. Inbound Process
(1) Conveyor Line & Rapid Docking Workstation Inbound
The upstream LES system issues putaway tasks received by the IMHS (Intelligent Material Handling System).
Upon arrival of qualified parts at the AS/RS, operators place task-associated containers at the infeed point of the receiving conveyor line.
Dimension Check: Dimension measuring devices inspect containers. Those not conforming to agreed designs are diverted to an exception handling point via the conveyor. Containers passing inspection have their barcodes read by scanners, reported to IMHS.
Conveyor Routing: The IMHS, coordinating with the conveyor system, determines the container's path. Containers are routed to a diversion point.
Robot Pickup (Conveyor): Containers routed to the conveyor diversion point trigger a robot call. Upon arrival, the robot interfaces with the conveyor line to pick up containers one by one, then departs to complete putaway.
Robot Pickup (Rapid Docking WS): Containers routed to the Rapid Docking Workstation enter via its infeed conveyor and elevator. When ready, the workstation calls a robot. Upon robot arrival, the workstation pushes all waiting containers simultaneously onto the robot's carrier basket. The robot then departs to complete putaway.
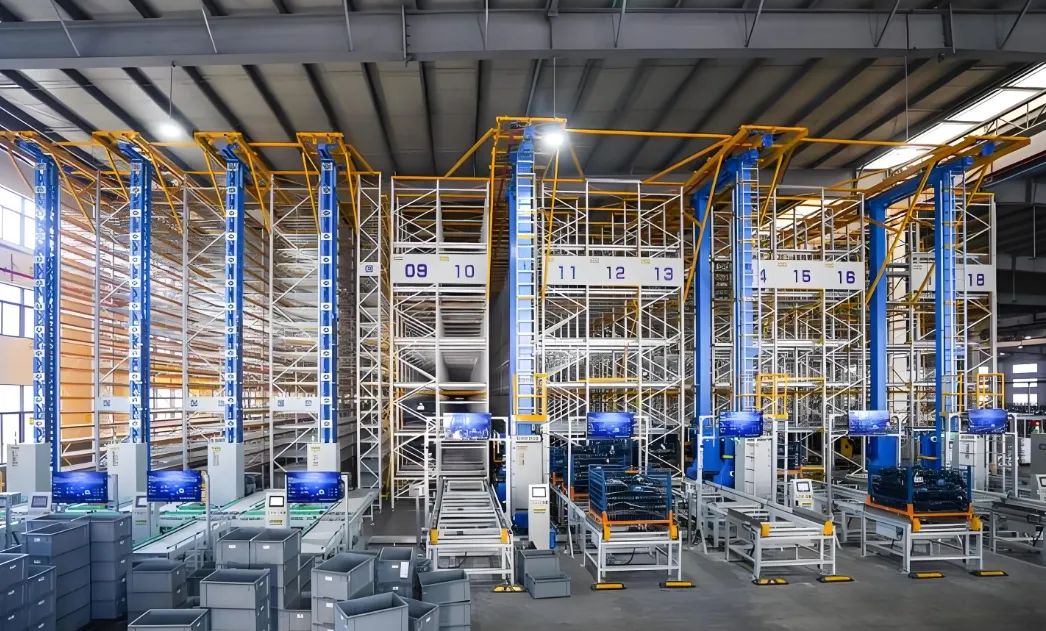

(2)Buffer Rack Inbound
Staff place containers individually onto buffer racks according to putaway requirements.
They manually scan the container label and rack bin code to bind them.
The upper-level scheduling system is notified to dispatch an Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR) to pick up the container for putaway into the AS/RS.
NAEC 2. Outbound Process
(1) Outbound via Conveyor Line & Rapid Docking Workstation
Robot Container Delivery: Robots transport containers to the outbound points (conveyor line infeed or Rapid Docking Workstation discharge point) based on order type.
Rapid Docking WS Discharge: Robots wait at the discharge point. The workstation retrieves containers from the robot's carrier basket in bulk to its internal buffer. An elevator transfers containers to the conveyor line until all are unloaded.
Automatic Barcode Reading: The conveyor line reads barcodes successfully and routes containers to picking stations, tracking container IDs.
Picking & Outbound: Containers flow to the picking station and pause. The system prompts the operator to confirm outbound information. Once full-container picking for an order is complete, the conveyor advances the next container to the station to continue fulfilling the current pull order.
(2) Outbound via Buffer Racking
Outbound Order Creation: Operators create outbound orders in the IMHS system by selecting material/containers, order type, and the destination GLES (Goods to Line Expediting Station) location.
Order Assignment: IMHS assigns orders to designated workstations based on order type. It splits picking tasks by container type and assigns them to corresponding buffer racks.
Inventory Allocation: IMHS locates containers for the order based on the specified materials and allocation strategy. It assigns an AMR to retrieve the container and deliver it to the buffer rack, lighting up the corresponding e-tag for operator identification.
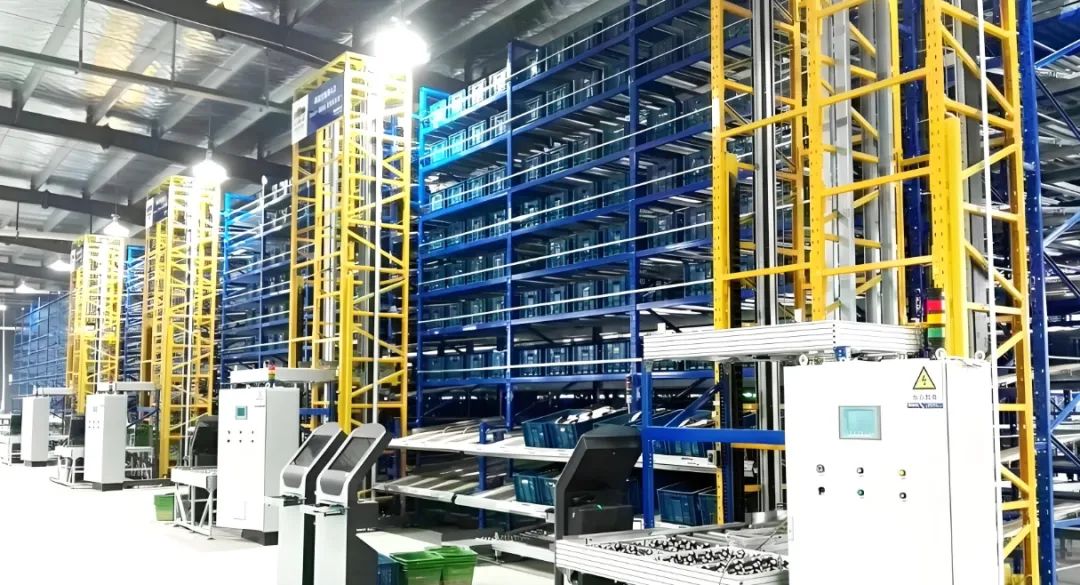

NAEC Intelligent Logistics' integrated Small-Parts Unmanned Warehouse AS/RS solution replaced numerous traditional logistics tasks performed by operators, including inbound scanning, putaway, material preparation, and outbound scanning. This significantly reduced labor costs. The dense storage configuration effectively utilized vertical space, increasing warehouse space utilization by 110%. Furthermore, robot automation and dynamic slotting replaced manual inventory counting and small parts storage location planning, optimizing these workloads.
Simultaneously, by adopting an unmanned, intelligent, and digital management model, the solution provides real-time visual displays of warehouse capacity, stock age, inbound/outbound flow, and storage location utilization. This offers intelligent support for improving production efficiency and product quality.
Recommended News
Sorry,当前栏目暂无内容!
您可以查看其他栏目或返回 首页
Sorry,The current column has no content!
You can view other columns or return Home
Address:No. 1, Zhongxing West Road, Lishui District, Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province
Copyright © Nanjing Autoweld Automation Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved
 Jiangsu Public Security Network Security Permit No. 32011502010584
Jiangsu Public Security Network Security Permit No. 32011502010584
Website Construction:www.300.cn Nanjing

Follow Us
 Group Company
Group Company